Introduction
The Alhambra in Granada, Spain, is more than just an architectural marvel; it’s a testament to centuries of history, culture, and art. Originally built as a fortress, it evolved into a majestic palace complex, reflecting the zenith of Moorish art and architecture. This travel guide delves into the fascinating history, main attractions, must-experience activities, and practical travel tips to help you make the most of your visit to this iconic landmark.
Historical Background
Origins and Construction
The Alhambra’s origins date back to 889 AD when it was initially constructed as a small
fortress. Its significant expansion began in the mid-13th century under the Nasrid emir Mohammed
ben Al-Ahmar, the founder of the Nasrid dynasty. The complex’s construction continued over the
next two centuries, turning it into a royal palace.
Moorish Period
During the Nasrid dynasty, the Alhambra became a symbol of the Islamic Golden Age in Spain. It
served as the residence of the Muslim rulers and their court, showcasing the pinnacle of Islamic
art and architecture in Western Europe. The intricate stucco work, lush gardens, and stunning
tile mosaics are testaments to this era’s artistic achievements.
Christian Reconquest
In 1492, the Alhambra witnessed a significant transition when the Catholic Monarchs, Ferdinand
and Isabella, conquered Granada. The Alhambra was transformed into a royal court, and
significant alterations were made, including the construction of the Renaissance-style Palace of
Charles V.
Modern Preservation
Today, the Alhambra is a UNESCO World Heritage site, meticulously preserved and restored to
reflect its historical grandeur. It stands as a symbol of cultural fusion, attracting millions
of visitors annually.
Main Attractions
The Courtyard of the Lions
The Courtyard of the Lions, or Patio de los Leones, is perhaps the most iconic part of the
Alhambra. This serene courtyard is named after the twelve marble lions that support the central
fountain. The intricate stucco work and slender columns surrounding the courtyard exemplify the
Nasrid architectural style.
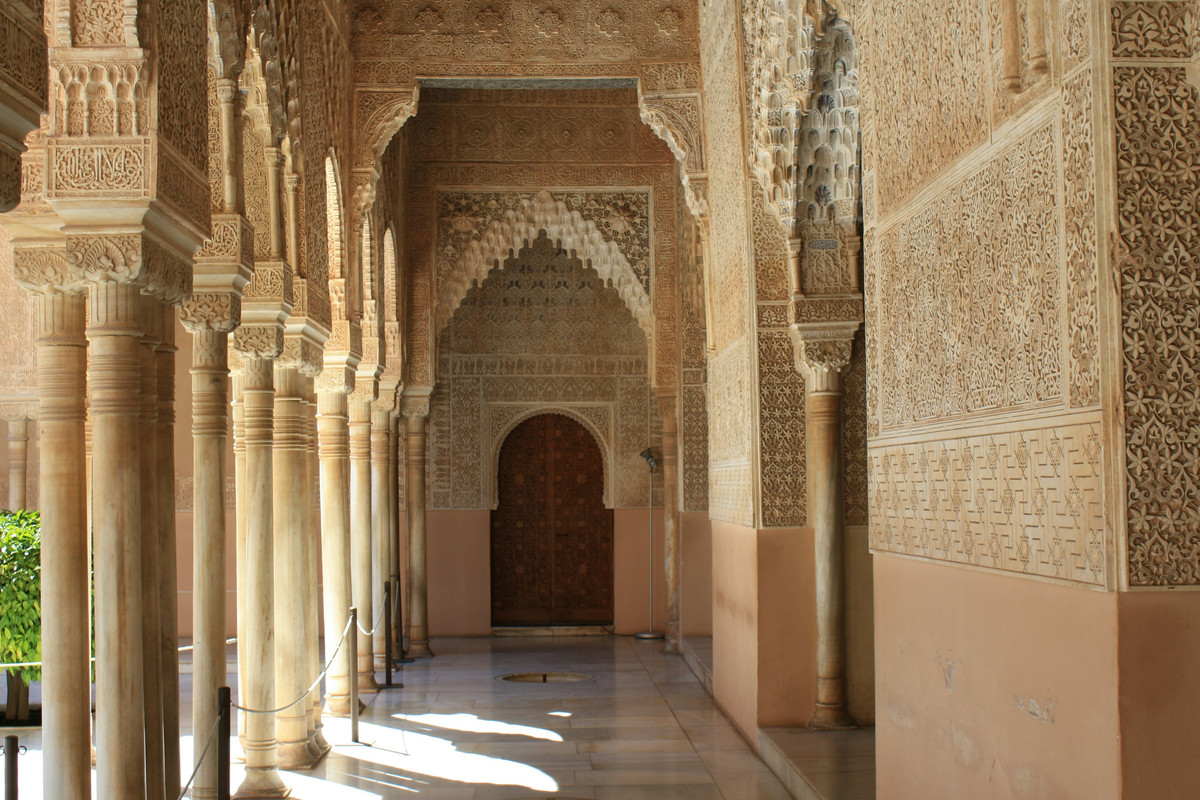

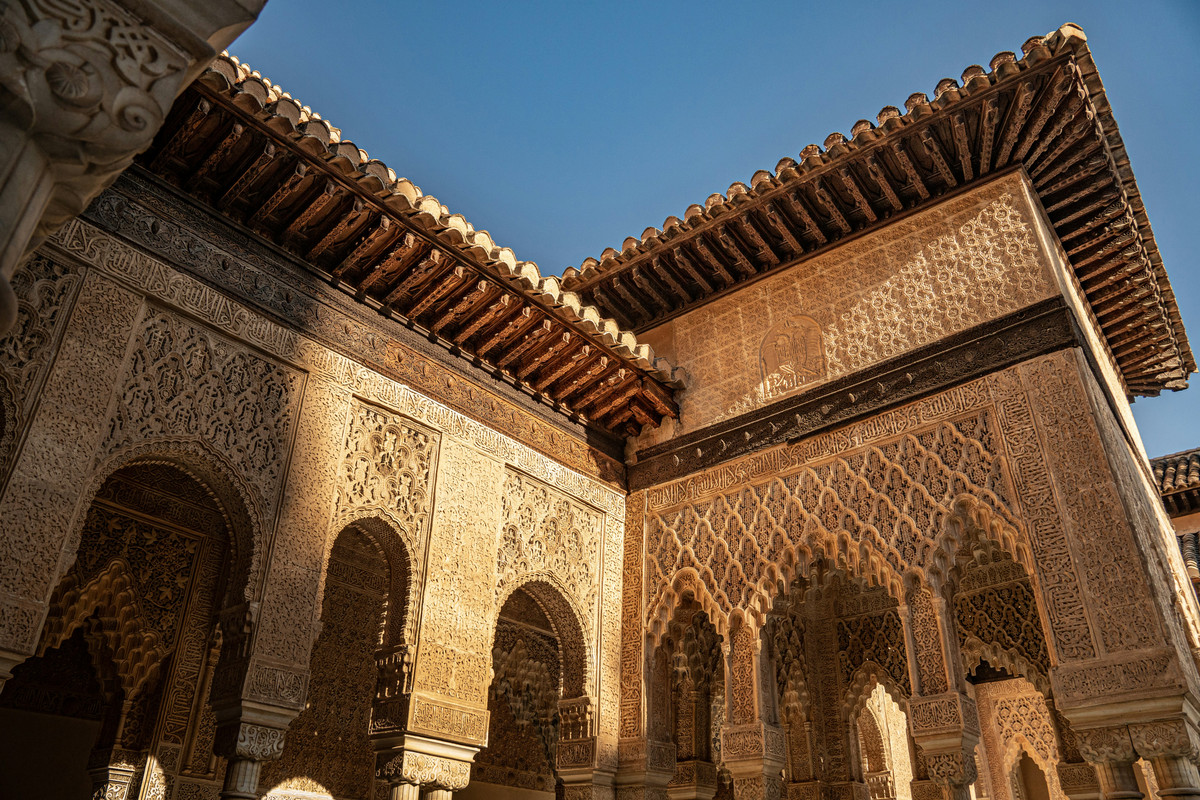
The Nasrid Palaces
The Nasrid Palaces are a series of interconnected buildings that served as the residence of the
Nasrid emirs. Highlights include the Hall of the Ambassadors, the largest room in the Alhambra,
known for its stunning wooden ceiling, and the Hall of the Two Sisters, famed for its elaborate
stalactite dome.

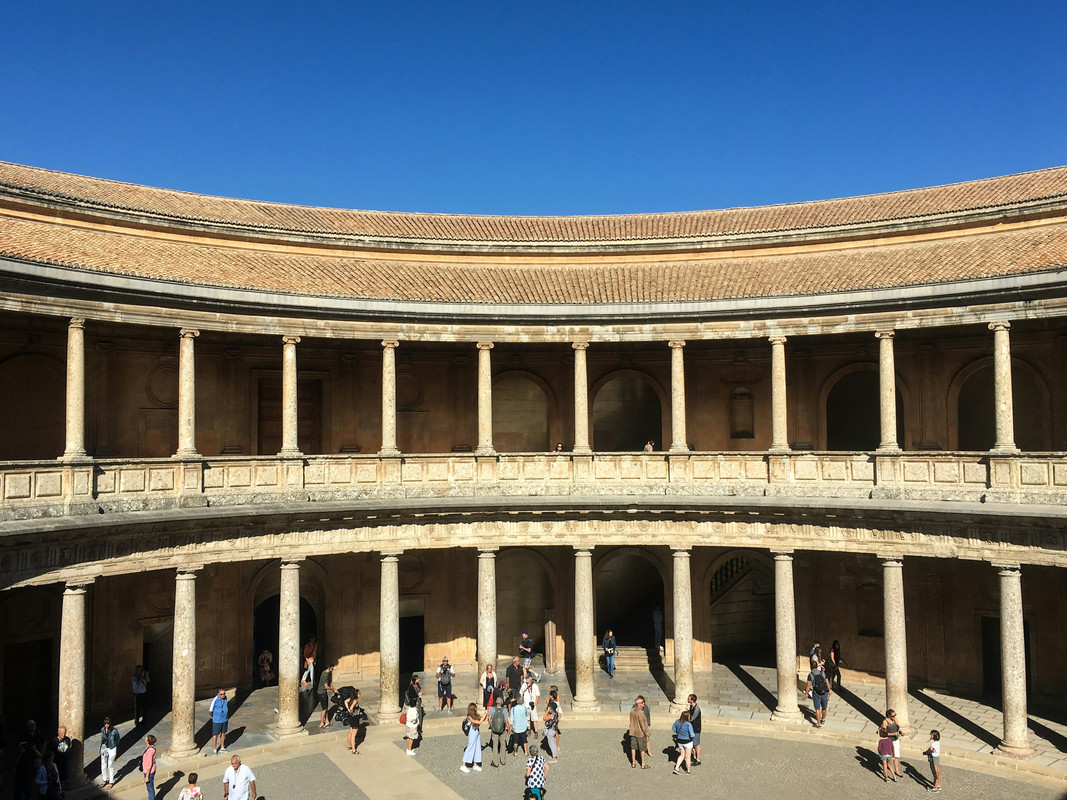
The Palace of Charles V
Built after the Christian reconquest, the Palace of Charles V stands out with its Renaissance
architectural style. This imposing structure houses the Alhambra Museum, which displays a
collection of artifacts from the Alhambra and Islamic art.

The Alcazaba
The Alcazaba is the oldest part of the Alhambra, serving as the original fortress. Its massive
towers, such as the Torre de la Vela, offer panoramic views of Granada and the surrounding
mountains. The military architecture and strategic placement highlight its defensive
significance.

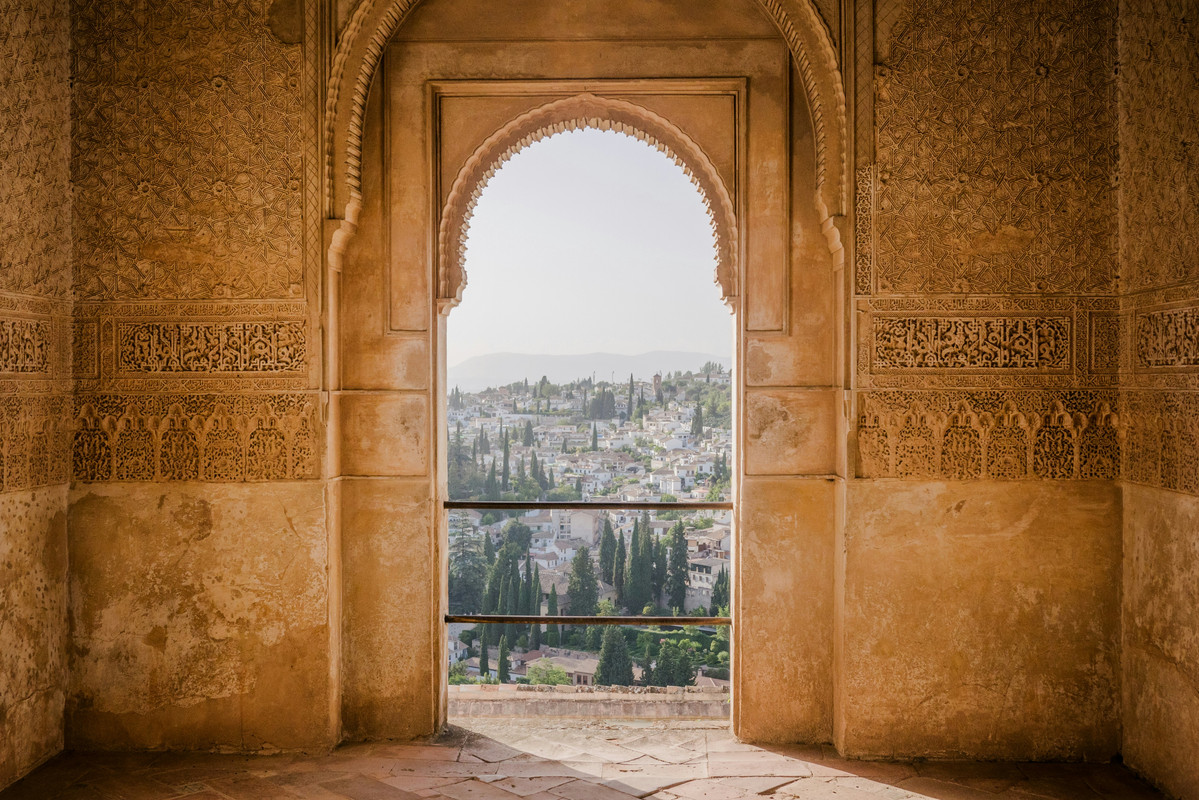
The Generalife Gardens
The Generalife Gardens, once the summer palace of the Nasrid rulers, are a haven of peace and
beauty. The gardens feature lush vegetation, water fountains, and intricate pathways, reflecting
the Islamic love for nature and tranquility.

Must-Experience Activities
Night Tours
Visiting the Alhambra at night offers a magical experience. The illuminated palaces and
courtyards create a mystical atmosphere, allowing visitors to appreciate the beauty of the
intricate designs in a different light.
Guided Tours
Opting for a guided tour can enrich your visit with detailed historical and architectural
insights. Knowledgeable guides can provide context to the intricate decorations and the
significance of various rooms and structures.
Photography Hotspots
The Alhambra is a photographer’s paradise. Key spots for capturing its beauty include the
panoramic views from the Alcazaba, the reflections in the Courtyard of the Myrtles, and the
intricate details in the Nasrid Palaces.
Architectural Design
Moorish Architecture
The Alhambra is a prime example of Moorish architecture, characterized by its use of geometric
patterns, intricate tilework, and stucco decoration. The harmony and balance in the design
reflect the Islamic principles of beauty and order.
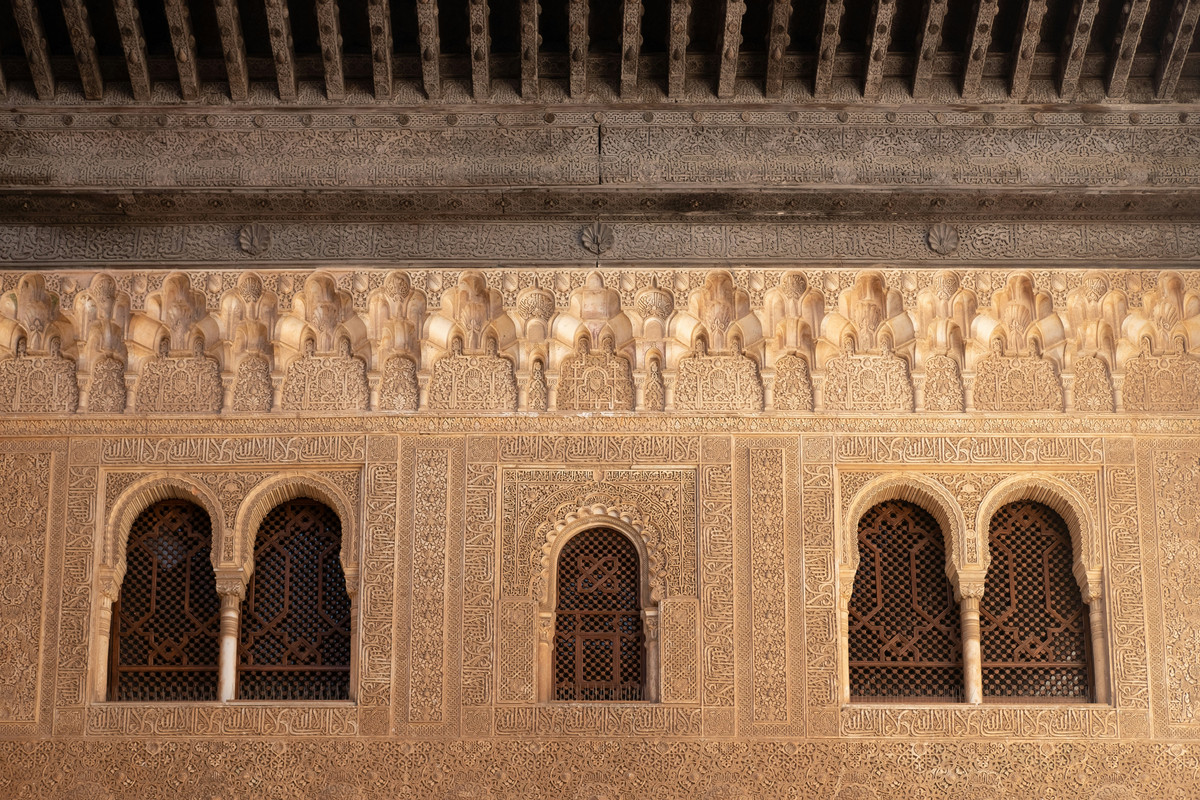
Decorative Arts
The decorative arts within the Alhambra are unparalleled. From the Arabic calligraphy that
adorns the walls to the muqarnas (stalactite) vaulting, each element is a work of art that
showcases the craftsmanship of the period.
Use of Water
Water plays a significant role in the Alhambra’s design. Fountains, reflecting pools, and
flowing channels are integral parts of the aesthetic and functional aspects of the palace,
symbolizing purity and life in Islamic culture.
Cultural Significance
Symbol of Islamic Heritage
The Alhambra stands as a symbol of Islamic heritage in Europe, representing the zenith of
Moorish culture and its contributions to art and architecture. It is a reminder of a time when
different cultures coexisted and influenced each other.
Influence on Modern Architecture
The architectural principles and decorative techniques of the Alhambra have influenced modern
architects and artists worldwide. Its emphasis on geometric design and intricate details
continue to inspire contemporary works.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
As a UNESCO World Heritage site, the Alhambra is recognized for its universal cultural value.
Its preservation is crucial for future generations to appreciate the rich history and artistic
achievements of the past.
Travel Tips
Visiting Hours and Ticket Booking
To avoid disappointment, it’s advisable to book your tickets well in advance, as the Alhambra
has a daily visitor limit. The site is open year-round, with varying hours depending on the
season.
Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit the Alhambra is during the spring and autumn months when the weather is
pleasant, and the gardens are in full bloom. Summer can be hot and crowded, while winter offers
a quieter experience.
Getting There
Granada is well-connected by train and bus from major Spanish cities. Once in Granada, the
Alhambra can be reached by taxi, bus, or a steep but scenic walk from the city center.
Dining and Accommodation
There are several dining options near the Alhambra, offering traditional Andalusian cuisine. For
accommodation, consider staying in the historic Albaicín district for a unique experience, with
many hotels offering views of the Alhambra.
Conclusion
The Alhambra is not just a historical monument but a journey through time, showcasing the blend of cultures and artistic excellence. Its intricate architecture, lush gardens, and rich history make it a must-visit destination. Embark on this journey to experience the magic and splendor of the Alhambra yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the opening hours of the Alhambra?
The Alhambra is open daily, with seasonal variations in opening hours. It’s best to check the official website for the most accurate information. -
How far in advance should I book tickets?
It’s recommended to book tickets at least a few weeks in advance, especially during peak tourist seasons. -
How long does a visit to the Alhambra take?
A comprehensive visit, including the Nasrid Palaces, Generalife Gardens, and Alcazaba, typically takes about 3 to 4 hours. -
Are guided tours available?
Yes, guided tours are available and highly recommended for a deeper understanding of the Alhambra’s history and architecture. -
What other attractions are near the Alhambra?
Nearby attractions include the Albaicín district, the Granada Cathedral, and the Royal Chapel of Granada.